FretFitter
A tool to compare fretting of clavichords or lengths of organ pipes with any temperaments and to calculate fretting distances. Initiated by the instrument maker Gregor Bergmann and available at https://gregor-bergmann.com/de/fretfitter.A description of the tool was published in the FoMRHI Quarterly No. 170, August 2025 of the Fellowship of Makers and Restorers of Historical Instruments. Current version 02.00 with additions for bridge angle and new table to show tunings in fractions of a comma.
Features
- Overview of Pythagorean and Syntonic Commas and Schisma with conversions of fractional values to cents.
- Fret Calculator to determine:
- Length of shorter string from the length of the longer string and the cents difference.
- Length of the longer string from the length of the shorter string and cents difference.
- Difference in cents from the lengths of the longer and shorter strings.
- A set of shorter string lengths, fret distances and cents difference from a pair of notes with the longer string notes for a given temperament.
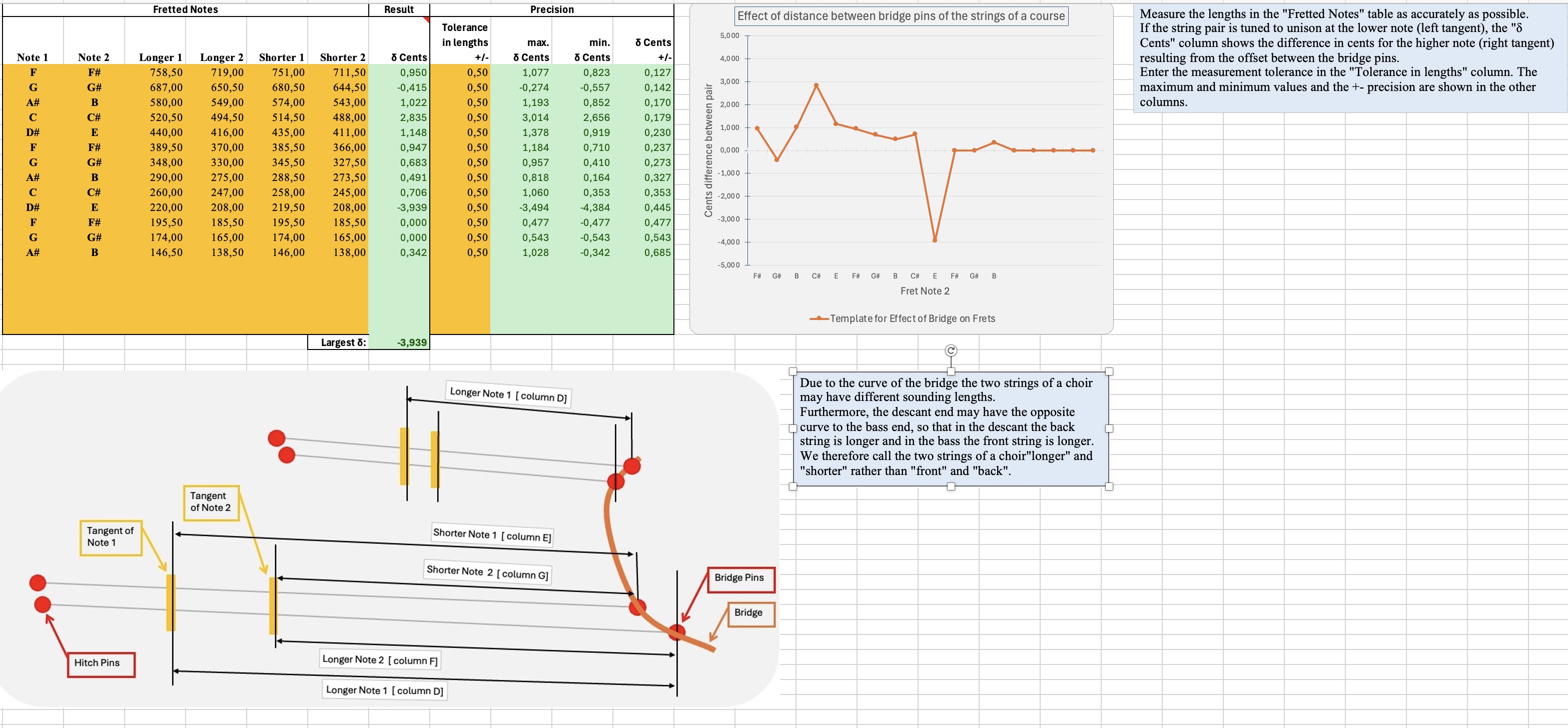
- Calculator to show the effect of the bridge angle on fretted notes.
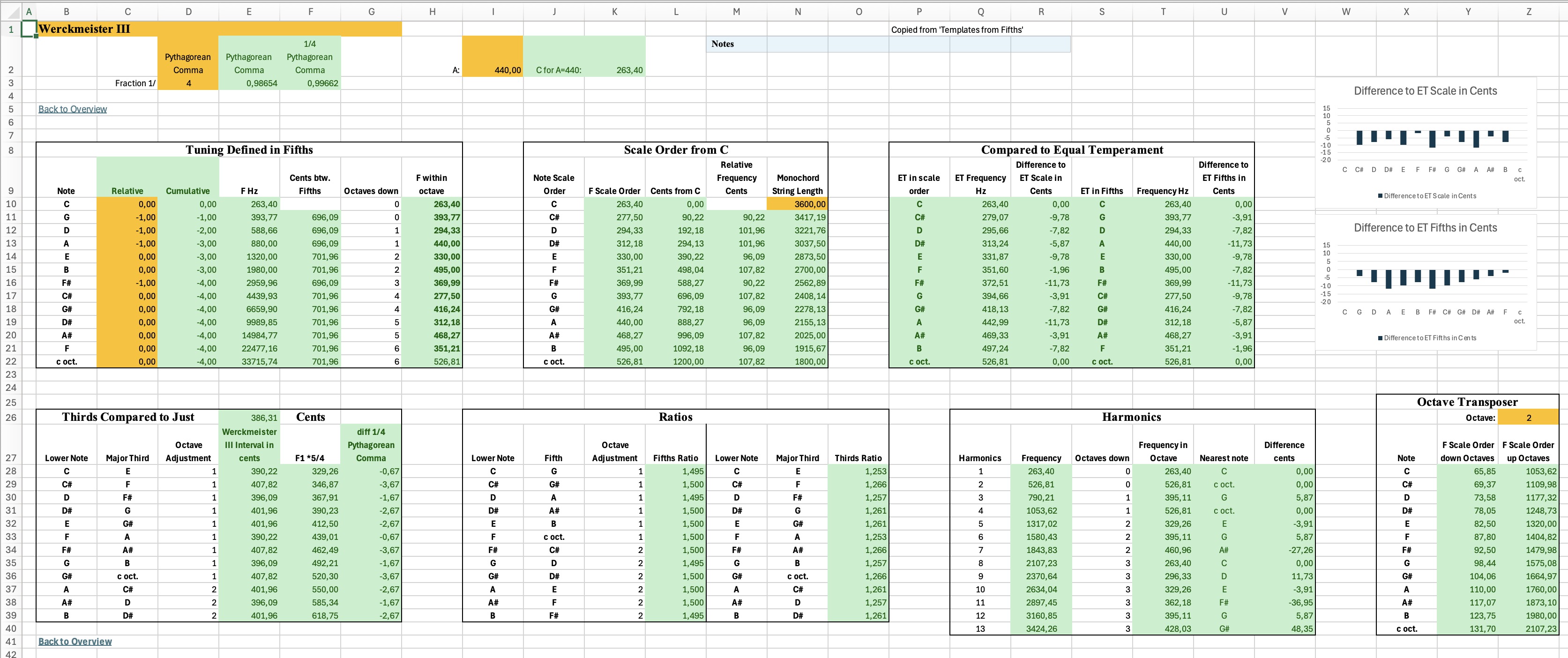
- Templates for defining temperaments in fifths or scale order, using fractions of commas, cents, or cents from equal temperament. These include:
- Choice of fractions of Pythagorean or Syntonic comma or cents.
- Setting of frequency of A, e.g. 440Hz.
- Setting of temperament for each note.
- Resulting frequencies.
- Listing in fifths and scale order.
- Comparison with equal temperament with graphs in fifths and scale order.
- Comparison of thirds to just intervals.
- Ratios of fifths and thirds (for comparison with just ratios of 1.5 and 1.25)
- List of harmonics with nearest note and difference in cents (to show that some harmonics do not fall on exact notes)
- Octave transposer to give frequencies in any octave
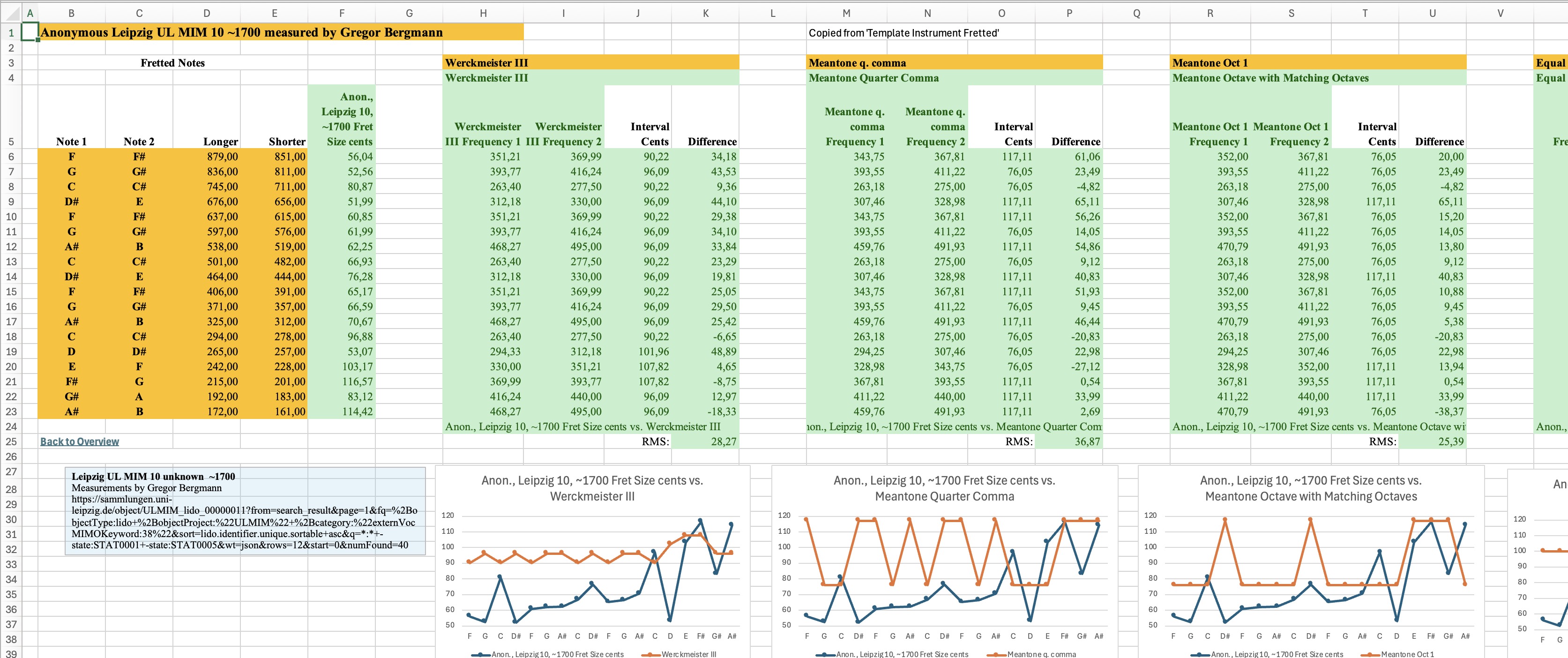
- Template for defining instruments from measured fret distances with:
- Comparisons with temperaments (as defined from templates above), in cents and graphically.
- Root mean square (RMS) of differences for comparison.
- Template for defining instruments from pipe or string lengths with:
- Entry of frequency of A.
- Entry of pipe or string lengths.
- Comparisons with four temperaments (as defined from templates above), both in cents and graphically.
- Comparison with equal temperament with graphs in fifths and scale order.
- Table to show fractions of a comma when instrument or temperament defined by lengths or relative to equal temperament.
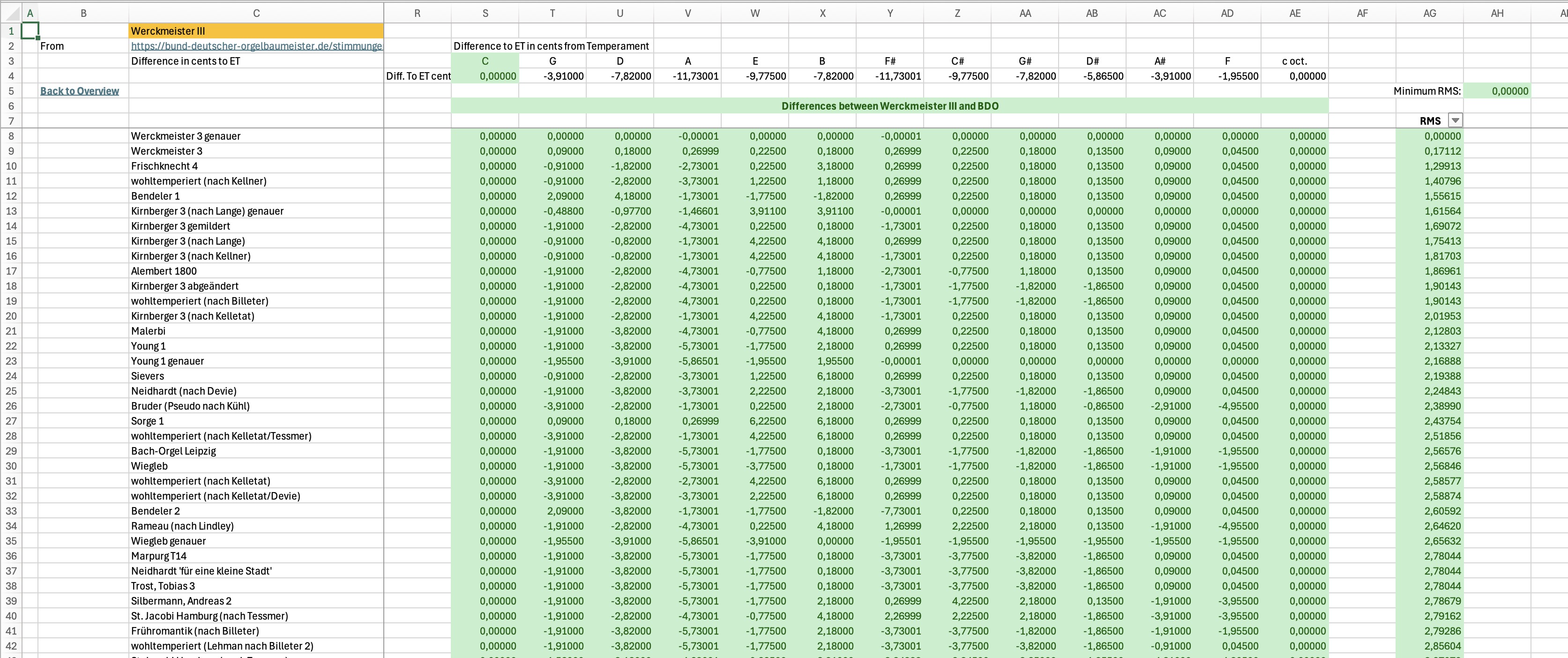
- A "wildcard" temperament sheet to use any of over 300 temperaments taken from a collection of the Bund Deutscher Orgelbaumeister (Association of German Master Organ Builders), who kindly gave us permission to use them.
- Best Fit sheets for Instruments and Temperaments which compare the selected instrument or temperament with all the BDO temperaments. This can be sorted to find the best fitting temperaments based on the RMS difference.
Examples
What is Fretting?
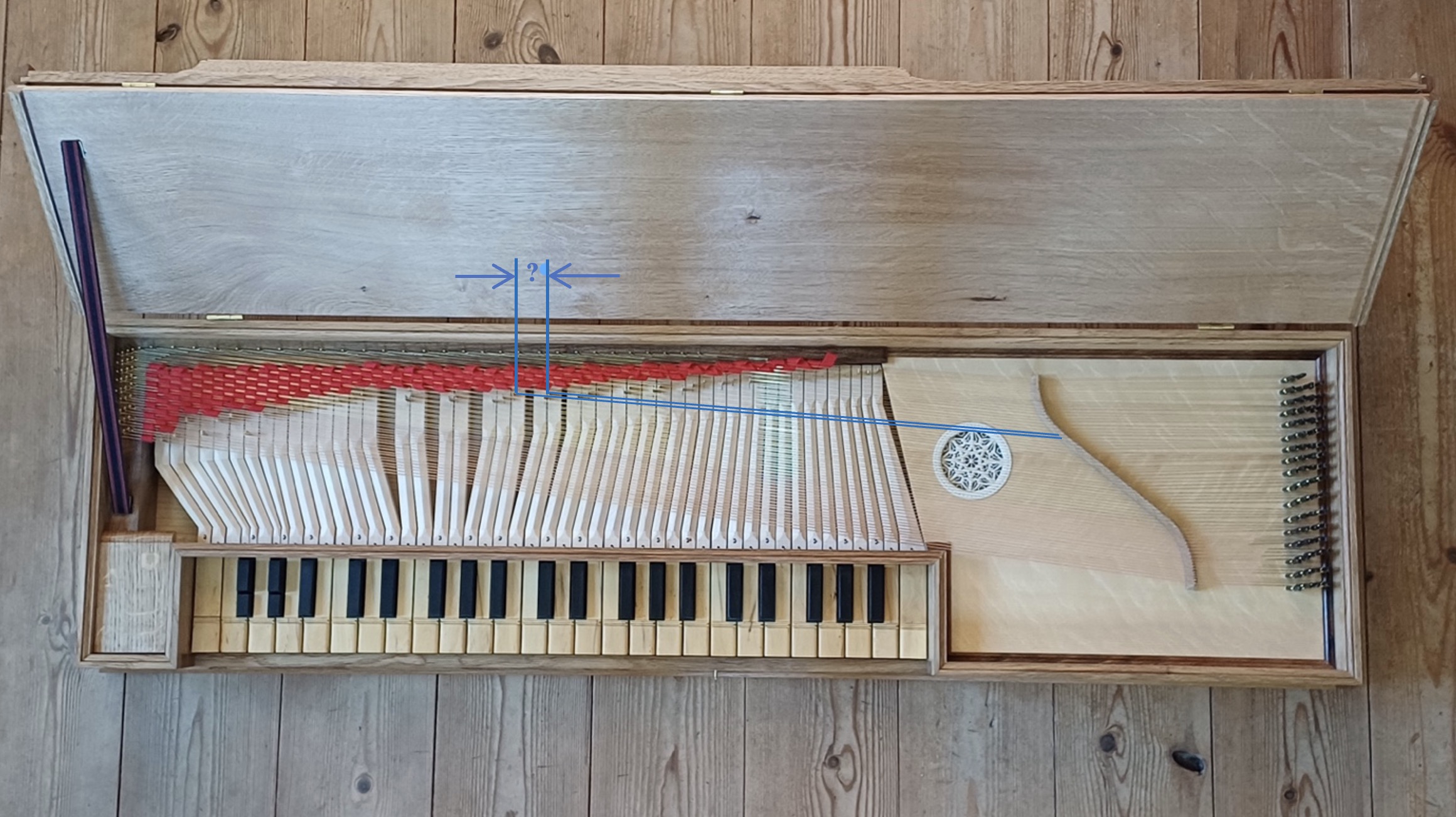

You may know about the frets on a guitar, the metal inlays on the neck which divide the string to give the notes of the scale.
A clavichord uses a metal tangent to strike and hold the string. The length between the tangent and the bridge on the right vibrates to give the tone while the left part of the string is damped with felt.
When the key is released, the felt damps the whole string and the sound stops.
Some instruments use the same string for neighbouring notes in the assumption that they would not be played simultaneously. To give the notes the correct tuning, the distance between the two tangents must be determined.
The image shows an instrument made by Gregor Bergmann.
A clavichord uses a metal tangent to strike and hold the string. The length between the tangent and the bridge on the right vibrates to give the tone while the left part of the string is damped with felt.
When the key is released, the felt damps the whole string and the sound stops.
Some instruments use the same string for neighbouring notes in the assumption that they would not be played simultaneously. To give the notes the correct tuning, the distance between the two tangents must be determined.
The image shows an instrument made by Gregor Bergmann.